PROCESS SYNCHRONIZATION
Experiment Number 1 : Counting Semaphores
Theory :
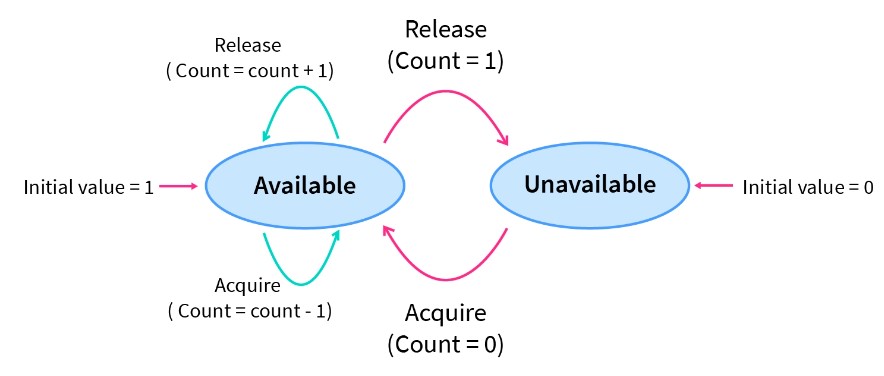
These are integer value semaphores and have an unrestricted value domain.
These semaphores are used to coordinate the resource access, where the semaphore count is the number of available resources.
If the resources are added, semaphore count automatically incremented and if the resources are removed, the count is decremented.
Where are Counting Semaphores Used?
There are situations where multiple processes must run in a key part at the same time.
When more than one process is required in the crucial part at the same time, counting semaphores might be employed.
Features of Counting Semaphore :
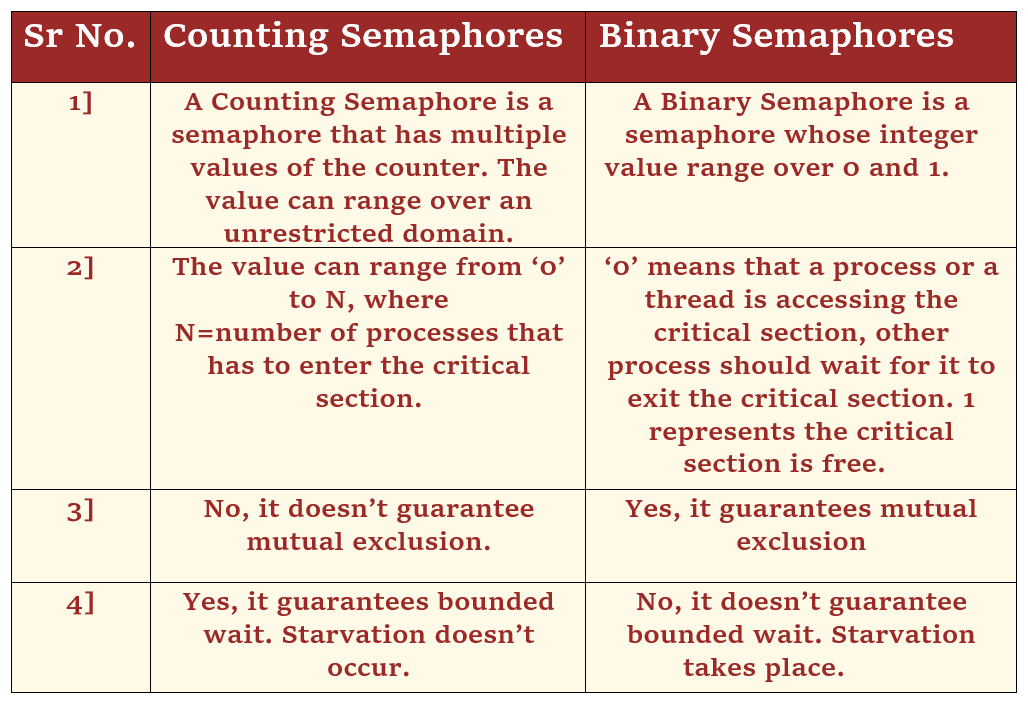
A counting semaphore refers to a semaphore with several counter values.
The value can span a wide range of possibilities.
It is a structure that consists of a variable known as a semaphore variable, which can accept more than two values, and a list of tasks or entities, which is nothing more than the process or thread.
The number of processes or threads authorised inside the crucial region is the value of the semaphore variable.
The counting semaphore’s value can range from 0 to N; wherein N is the number of processes that are free to enter or exit the crucial area.
As previously stated, several processes or threads can access the crucial region of a counting semaphore; hence mutual exclusion also isn’t guaranteed.
Counting semaphores assures bounded wait since numerous instances of the process can use the shared resource at the same time.
A process that enters the crucial section must wait for the other process to enter the critical section using such a semaphore, suggesting that no process will starve.